6-Mercaptopurine IUPAC Nomenclature, SAR, Physicochemiscal properties, Synthesis, Mechanism of Action and Uses. In our exploration of Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR), understand how 6-Mercaptopurine’s purine analog nature interferes with nucleic acid synthesis, inhibiting cell proliferation. Explore the intricate synthesis routes, unveiling the transformation from 7H-Purin-6-ol and 6-Chloropyrimidine-4,5-diamine.
IUPAC nomenclature
3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione
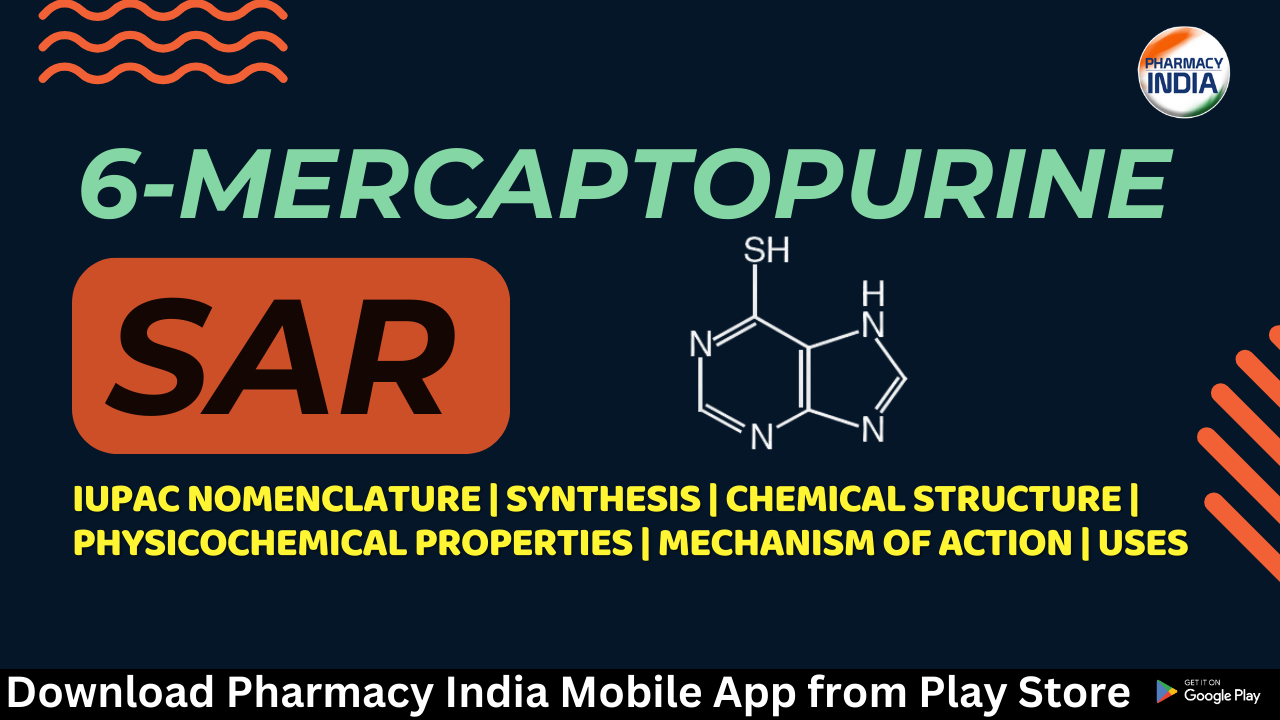
Chemical Structure

Physicochemical properties
1. Chemical formula: C5H4N4S
2. Molar mass: 152.18 g/mol
3. Solubility: 6-Mercaptopurine is sparingly soluble in water.
4. Melting Point: The melting point of 6-Mercaptopurine is approximately 314-315°C.
5. pKa: The pKa values of the functional groups in 6-Mercaptopurine are approximately 1.96, 7.96, and 9.52.
6. Appearance: 6-Mercaptopurine is a yellow to yellow-green crystalline powder.
7. Storage Conditions: It should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from light and moisture.
8. Stability: 6-Mercaptopurine is sensitive to light and moisture. It should be stored in a tightly closed container and protected from exposure to light.
9. Hygroscopicity: It may absorb moisture from the air.
SAR of 6-Mercaptopurine
1. Purine Analog: 6-MP is a purine analog, which means it structurally resembles the purine bases found in DNA and RNA. This structural similarity allows 6-MP to interfere with nucleic acid synthesis and inhibit cell proliferation. The purine scaffold is essential for its activity, as it enables the compound to participate in crucial biological processes.
2. Thiol Group: 6-MP contains a thiol (sulfhydryl) group (-SH) which is important for its activity. This group is involved in various biochemical reactions, including the formation of covalent bonds with cellular targets. The thiol group is also significant for its role in redox reactions within the cell.
3. Metabolism: 6-MP undergoes extensive metabolism in the body, including conversion to active metabolites such as 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGNs). These metabolites are incorporated into DNA and RNA, leading to interference with nucleic acid synthesis and cell death. Enzymes like thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) are involved in these metabolic pathways, and variations in these enzymes can affect the efficacy and toxicity of 6-MP.
4. Electron Delocalization: The conjugation and delocalization of electrons in the purine ring system contribute to the stability and reactivity of 6-MP and its metabolites. This electron delocalization can affect the compound’s interactions with cellular targets.
5. Electrophilic Nature: The thiol group in 6-MP makes it electrophilic, allowing it to react with nucleophiles in the cell, leading to the formation of covalent bonds with cellular biomolecules. This reactivity is essential for its mechanism of action.
6. Selective Toxicity: The SAR of 6-MP also involves achieving selective toxicity, meaning it should target cancer cells or cells involved in autoimmune responses more than normal, healthy cells. Achieving this selectivity is a complex interplay of the compound’s structure and the specific vulnerabilities of the target cells.
Synthesis
Route-I. From: 7H-Purin-6-ol

Route-II. From: 6-Chloropyrimidine-4,5-diamine

Mechanism of action
Mercaptopurine (6-MP) is converted to an active metabolite which gets incorporated into the DNA and inhibits purine synthesis and thereby protein synthesis.
Uses
1. Acute leukaemias in children
2. Choriocarcinoma
3. Solid Tumours
Acetazolamide: SAR, Synthesis, Mechanism, and Uses
Methotrexate: SAR, Synthesis, Mechanism, and Uses
Triprolidine SAR, Physicochemical Properties, Synthesis, IUPAC Nomenclature, Mechanism of action and Uses
Promethazine HCl SAR, Physicochemical Properties, IUPAC Nomenclature, Mechanism of action and Uses
Cimetidine SAR, Physicochemical Properties, IUPAC Nomenclature, Mechanism of action and Uses
Download B. Pharma 1st Semester Model Papers
B. Pharma 4th Semester Model Papers
Subscribe our PHARMACY INDIA Youtube Channel for more Pharma Updates
Click here to follow us on Instagram
Click here to Join our Telegram Channel
Download PHARMACY INDIA MOBILE APP from Google Play Store