IUPAC nomenclature
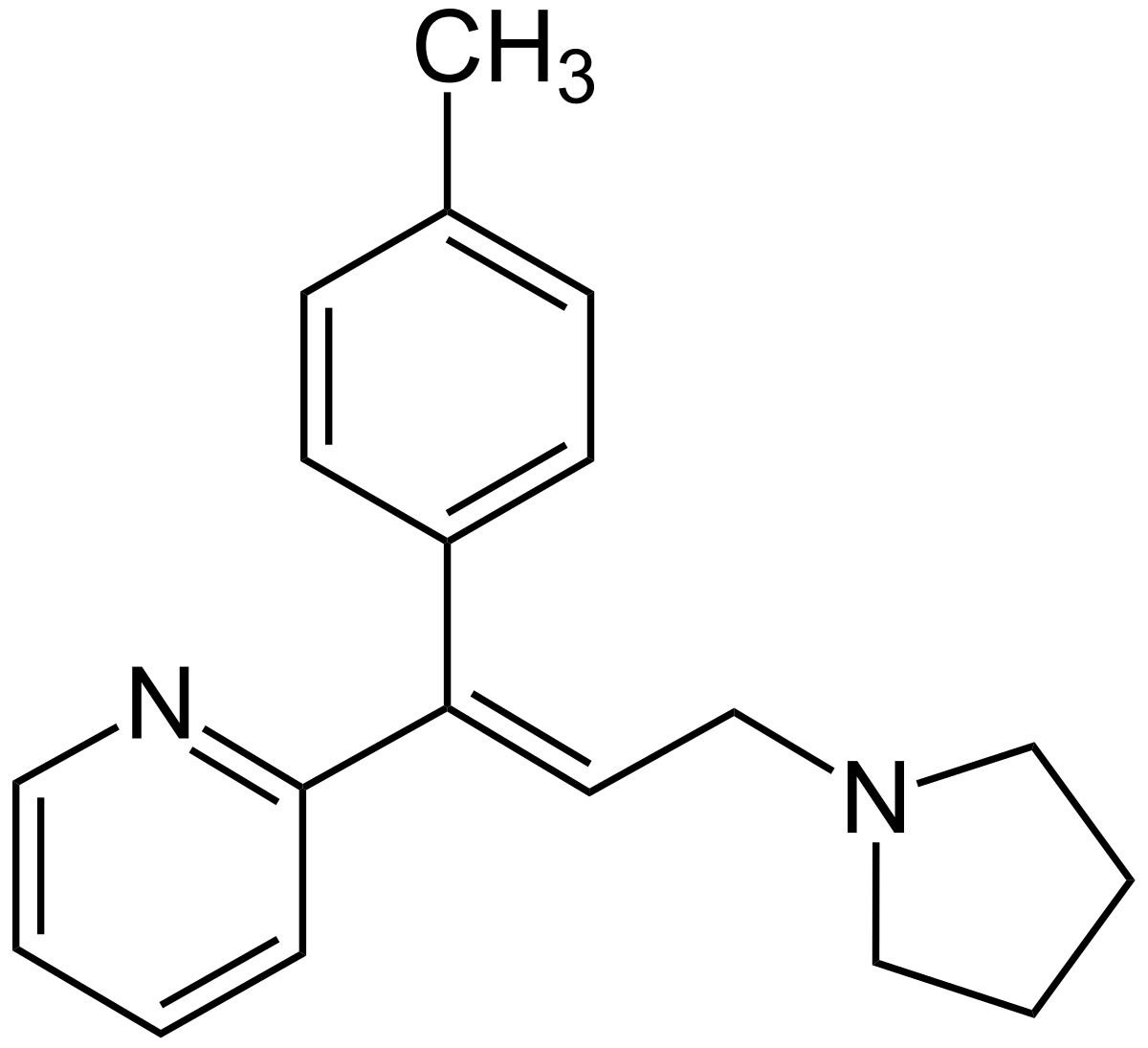
2-[(E)-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-pyrrolidin-1-yl-prop-1-enyl]pyridine
Chemical Structure
Physicochemical Properties
1. Molecular Formula: C19H22N2
2. Molecular Weight: 278.39 g/mol
3. Melting Point: The exact melting point of triprolidine may vary depending on the specific form of the compound (e.g., salt or crystalline structure). Generally, it is around 147-150°C.
4. Solubility: Triprolidine is sparingly soluble in water but is more soluble in organic solvents like chloroform and ethanol.
5. Acidity/Basicity: Triprolidine is a weak base. Its basicity is due to the presence of the amine group in its structure.
6. Partition Coefficient (LogP): The octanol/water partition coefficient, often denoted as LogP, is a measure of a compound’s hydrophobicity. Triprolidine has a LogP value indicating it is lipophilic, meaning it has a higher affinity for fat/lipid-based environments than water.
SAR of Triprolidine
1. Amine Group: Triprolidine contains an amine group (-NH2) in its structure. This amine group is essential for its activity as an antihistamine. Amines often act as bases and can participate in hydrogen bonding interactions, which might be crucial for binding to histamine receptors.
2. Arylalkylamine Structure: Triprolidine belongs to the class of compounds known as alkylphenylamines. This specific structural motif, where an aryl group (phenyl) is connected to an alkylamine moiety, is common in many antihistamines. This structure seems to confer antihistaminic activity.
3. Stereochemistry: Triprolidine is a chiral molecule, meaning it has mirror-image stereoisomers (enantiomers). The specific stereochemistry can influence the interaction with biological receptors. In the case of triprolidine, the stereochemistry of the molecule is important for its activity. The marketed drug is typically a single stereoisomer.
4. Substituents on the Phenyl Ring: The specific substituents attached to the phenyl ring can influence the potency, selectivity, and duration of action of the antihistamine. Different substitutions can lead to variations in the drug’s affinity for histamine receptors and other biological targets, affecting its overall pharmacological profile.
5. Electron Density and Charge Distribution: The electron density and charge distribution within the molecule can influence its interaction with biological targets. These factors are determined by the arrangement of atoms and functional groups in the molecule.
6. Lipophilicity: The lipophilicity of the molecule, often represented by the octanol/water partition coefficient (LogP), can affect the drug’s absorption, distribution, and overall pharmacokinetics. This property is influenced by the presence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups in the molecule.
Synthesis
Mechanism of Action
1. Histamine Receptors: Histamine mediates its effects by binding to specific receptors in the body. There are several types of histamine receptors, and H1 receptors are particularly important in the context of allergic responses. When histamine binds to these receptors, it triggers a series of reactions that lead to allergy symptoms.
2. Antagonism of H1 Receptors: Triprolidine is an antagonist at H1 receptors. This means that it competes with histamine for binding to these receptors but does not activate the receptor. By binding to H1 receptors without activating them, triprolidine prevents histamine from binding and exerting its effects.
Uses
1. Nasal Congestion
2. Sneezing
3. Runny Nose
4. Itching and Watery Eyes
5. Itchy Throat or Skin
Acetazolamide: SAR, Synthesis, Mechanism, and Uses
Methotrexate: SAR, Synthesis, Mechanism, and Uses
Promethazine HCl SAR, Physicochemical Properties, IUPAC Nomenclature, Mechanism of action and Uses
Cimetidine SAR, Physicochemical Properties, IUPAC Nomenclature, Mechanism of action and Uses
Download B. Pharma 1st Semester Model Papers
B. Pharma 4th Semester Model Papers
Subscribe our PHARMACY INDIA Youtube Channel for more Pharma Updates
Click here to follow us on Instagram
Click here to Join our Telegram Channel
Download PHARMACY INDIA MOBILE APP from Google Play Store



